
ESG Data Management: Challenges, Opportunities, and Its Importance
- May 22, 2024
- OHI

In today’s corporate landscape, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) data management plays a pivotal role in shaping sustainable business practices. As companies transition from shareholder capitalism to stakeholder capitalism, the demand for transparency, accountability, and ethical decision-making has intensified. Let’s delve into what ESG data management entails, its significance, and how it can be leveraged for competitive advantage.
ESG data management involves collecting, verifying, analyzing, and reporting data related to a company’s operations and activities from an ESG standpoint. This encompasses aspects such as carbon emissions, resource utilization, labor practices, and corporate governance. The ultimate goal is to provide a clear and accurate picture of an organization’s ESG performance, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and companies to identify areas for improvement and sustainable growth. Beyond regulatory compliance, effective ESG data management significantly impacts corporate reputation and investor attraction.
Challenges:
Opportunities:
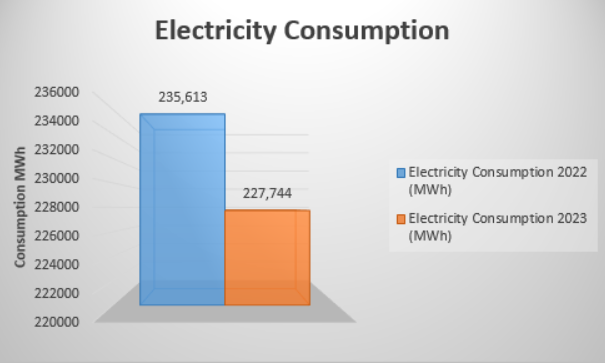
Sample1 – Comparative report of energy (electricity) consumption of a building, designed to showcase the decrease in energy usage consumption.
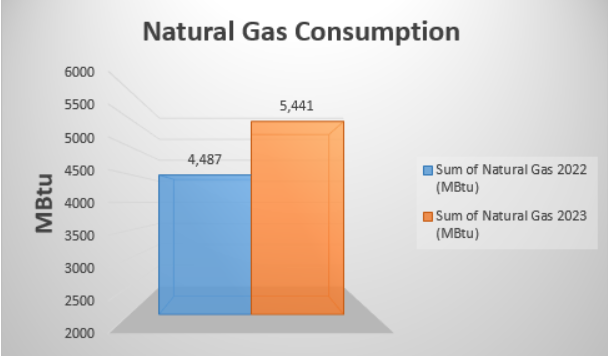
Sample 2 – Comparative report of natural gas consumption of an organization, required in GRESB certification
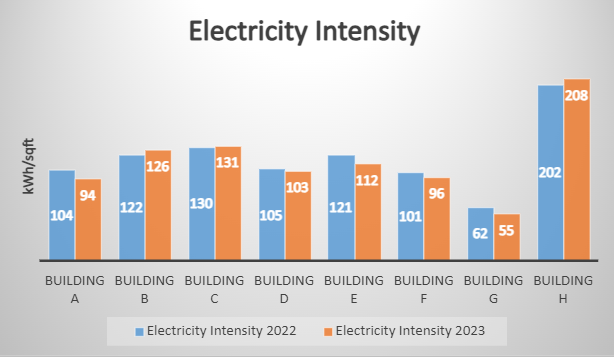
Sample 3– Comparative analysis of electricity intensity of different buildings owned/managed by an organization, required for annual reporting
ESG data management is not merely a compliance exercise; it’s a strategic imperative. By embracing it, companies can navigate the complexities of sustainability, drive innovation, and build a resilient future.
Remember, ESG data management isn’t just about numbers—it’s about shaping a better world for all stakeholders. 🌎🌱
Contact us for a customized NO OBLIGATION proposal for outsourcing your accounting activities.









