
The Ultimate Guide to ESG Data Management: Strategies for Success
- October 11, 2024
- OHI

In the current corporate environment, the significance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors cannot be overstated. Businesses are under growing scrutiny regarding their societal and environmental impacts. To navigate this landscape successfully, organizations must prioritize effective ESG data management. This is essential for enhancing corporate accountability and improving sustainability reporting. This guide delves into the core elements of ESG data management, offering valuable insights into best practices and strategic approaches for implementation.
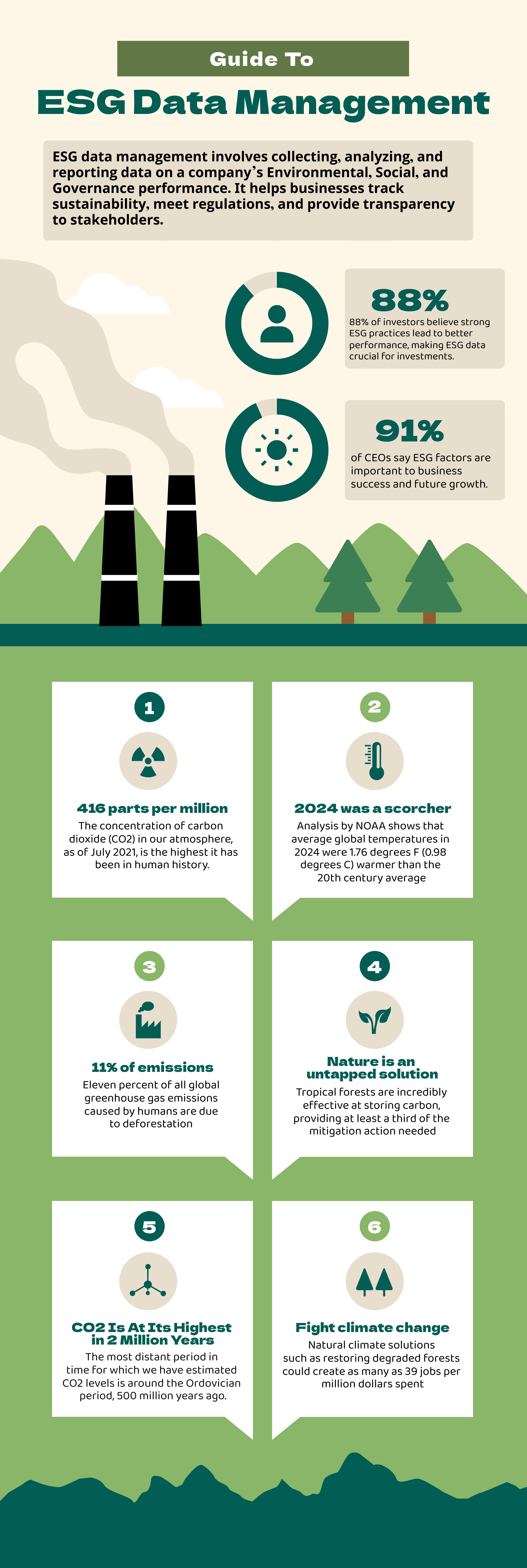
ESG data management refers to the processes and systems used to collect, analyze, and report data related to a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance. This data is critical for stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulatory bodies, who seek transparency and accountability in corporate practices.

Collecting accurate and relevant data is the foundation of effective ESG data management. This involves:
Once data is collected, the next step is analysis. This includes:
Effective reporting is essential for communicating ESG performance to stakeholders. This involves:
Implement a governance framework that outlines roles and responsibilities for ESG data management. This should include:
Utilize technology solutions to streamline ESG data management processes. Consider:
Encourage a company-wide culture that prioritizes sustainability and ESG considerations. This can be achieved through:
ESG data management is an ongoing process. Regularly review and refine data management practices by:

Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of ESG data can be challenging, especially when sourcing from multiple platforms. Companies must invest in data validation processes to maintain high standards.
As ESG regulations continue to evolve, organizations must stay informed and adapt their data management practices to remain compliant.
Effective ESG data management requires dedicated resources, including personnel and technology. Companies must prioritize ESG initiatives within their budgets.

Effective ESG data management is essential for companies committed to corporate responsibility and sustainability reporting. By establishing robust data collection, analysis, and reporting processes, organizations can enhance transparency, build stakeholder trust, and drive long-term value. Embracing best practices and leveraging technology will position companies to meet the growing demands of the ESG landscape, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
Contact us for a customized NO OBLIGATION proposal for outsourcing your accounting activities.









