
Understanding the Importance of Data Security in Accounting Outsourcing
- May 28, 2024
- OHI

In today’s interconnected business environment, more and more companies are opting accounting outsourcing to external service providers. This strategy can offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, access to expert knowledge, and increased efficiency. However, this shift also presents significant risks, particularly in the realm of data security. Ensuring the protection of sensitive financial information is critical, not only to comply with legal standards but also to maintain the trust of clients and stakeholders.
Accounting data is particularly sensitive because it contains detailed financial information about a business, including bank account details, employee information, customer data, and proprietary financial insights. In the hands of cybercriminals, such data can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, and even corporate espionage.
The consequences of a data breach can be devastating. Financial losses, legal liabilities, damaged reputations, and lost business are just a few of the potential outcomes. For instance, if sensitive data is leaked, it could lead to a loss of customer trust, which is incredibly difficult to regain. Moreover, companies may face regulatory fines and legal action if they fail to comply with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
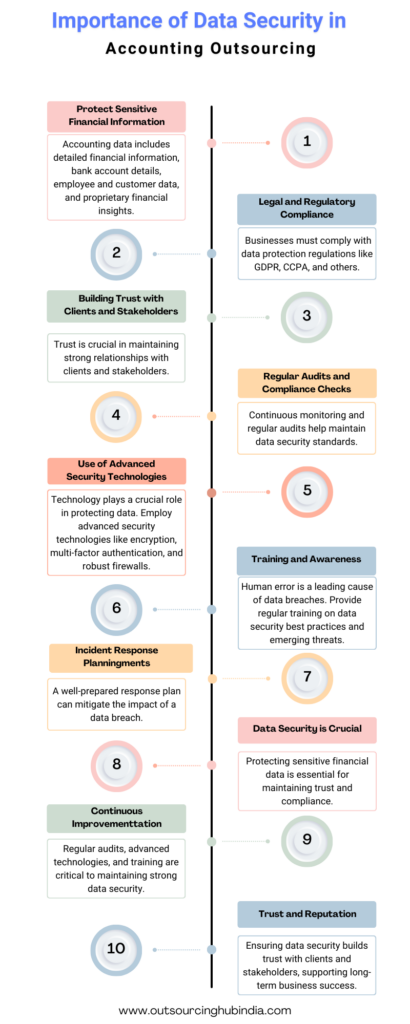

In conclusion, while outsourcing accounting functions can provide substantial benefits, it is imperative to manage the associated risks effectively, particularly those related to data security. By adhering to these principles and best practices, companies can safeguard their sensitive data, maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, and build trust with their clients and partners. Ensuring robust data security measures in place is not just a technical necessity; it’s a strategic imperative in today’s digital landscape.
Contact us for a customized NO OBLIGATION proposal for outsourcing your accounting activities.









